Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 Founders Edition Review
Every couple of years, Nvidia unveils a powerhouse graphics card—an exorbitantly priced marvel that catapults PC gaming into a new era. The Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 is precisely that, but its approach to next-generation performance is refreshingly unconventional. In many games, the performance boost over the RTX 4090 isn't as dramatic as expected, at least without DLSS Frame Generation. However, the next generation of Nvidia's DLSS, encompassing both upscaling and frame generation, delivers breathtaking leaps in image quality and performance—a jump even more significant than typical generational upgrades.
The RTX 5090's upgrade value hinges on your gaming habits: the games you play, your monitor's resolution and refresh rate, and your comfort level with AI-generated frames. For those with anything less than a 4K, 240Hz display, this upgrade might be unnecessary. But for high-end display owners, the AI-generated frames offer a tantalizing glimpse into the future of gaming.
Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 – Photos





RTX 5090 – Specs and Features
The Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 leverages Blackwell, Nvidia's high-end architecture powering data centers and supercomputers behind many popular AI models. This hints at the RTX 5090's strengths, but Nvidia hasn't neglected the non-AI aspects.
Nvidia managed to pack more Streaming Multiprocessors (SMs) into the same number of GPCs (Graphics Processing Clusters), resulting in a significant increase in CUDA cores—21,760, a 32% jump from the RTX 4090's 16,384. This substantial increase in shader cores fuels a large portion of the raw gaming performance improvement.
Each SM boasts four Tensor Cores and one RT Core, mirroring its predecessor. This translates to 680 Tensor Cores and 170 RT cores, compared to the RTX 4090's 512 and 128, respectively. The 5th-generation Tensor Cores are optimized for AI performance, now supporting FP4 operations, reducing VRAM dependence in AI workloads.

This powerful silicon is paired with 32GB of GDDR7 VRAM, a generational leap from the RTX 4090's GDDR6X. GDDR7 offers improved speed and power efficiency, although the RTX 5090's staggering 575W power draw (a significant increase over the 4090's 450W) indicates power efficiency wasn't the primary design goal.
The enhanced efficiency of the new Tensor Cores allowed Nvidia to transition the entire DLSS algorithm to a Transformer Neural Network (TNN) from a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). This shift doesn't necessarily boost frame rates with DLSS enabled, but Nvidia claims it improves image quality and reduces artifacts like ghosting.
Beyond the internal DLSS improvements, Nvidia introduces Multi-Frame Generation, a refined version of the Frame Gen technology from the RTX 4090. It's more efficient, smoother, and generates multiple frames from each rendered image, drastically improving frame rates. Similar to its predecessor, it's best enabled when a decent base frame rate is already achieved.
Purchasing Guide
The Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 launched January 30th, starting at $1,999. Remember, this is the Founders Edition price; third-party cards can be considerably more expensive.
The Founders Edition
The RTX 5090 demands 575W, far exceeding the RTX 4090's 450W. This increased power consumption translates to more heat, necessitating robust cooling. Previous Founders Editions were bulky, triple-slot behemoths. Surprisingly, the RTX 5090 is smaller, fitting into a dual-slot chassis with a dual-fan configuration.

During testing (including standard benchmarks and games with DLSS 4 and multi-frame generation), temperatures peaked around 86°C, even with power consumption reaching 578W. While high (higher than the RTX 4090's 80°C), it remained below throttling levels.
Nvidia achieved this compact design by centrally positioning a smaller PCB within the card, flanked by two fans and a heatsink spanning the card's width. Air intake is from the bottom, expelled through the top, relying on the PC case's exhaust fans. Unlike previous generations, there are no exhaust vents under the rear output ports.
The design aesthetics echo previous generations, featuring a central silver 'X' design similar to the RTX 4090, a gunmetal-gray chassis, and a white LED-lit 'GeForce RTX' logo.

The power connector, while resembling the 12VHPWR connector of the previous generation, is a new 12V-2x6 connector, claimed to be more efficient. It's angled towards the back for easier cable connection, appearing more secure.
Nvidia includes a 12V-2x6 adapter requiring four 8-pin PCIe power connectors to deliver the necessary 575W. This design allows compatibility with smaller PC cases, unlike previous generations, though third-party designs will likely be larger.
DLSS 4: Fake Frames?
Nvidia initially claimed up to 8x performance boosts with the RTX 5090. While not quite that high, it achieves extremely high frame rates in demanding games, primarily through frame generation. While the RTX 5090 offers a decent raw rasterization performance increase, the true next-generation benefit lies in its frame generation capabilities.
DLSS 4 introduces 'Multi-Frame Generation,' an enhanced version of DLSS 3's Frame Generation. The key is a new AI Management Processor (AMP) core, enabling more efficient workload distribution across the GPU, traditionally handled by the CPU.
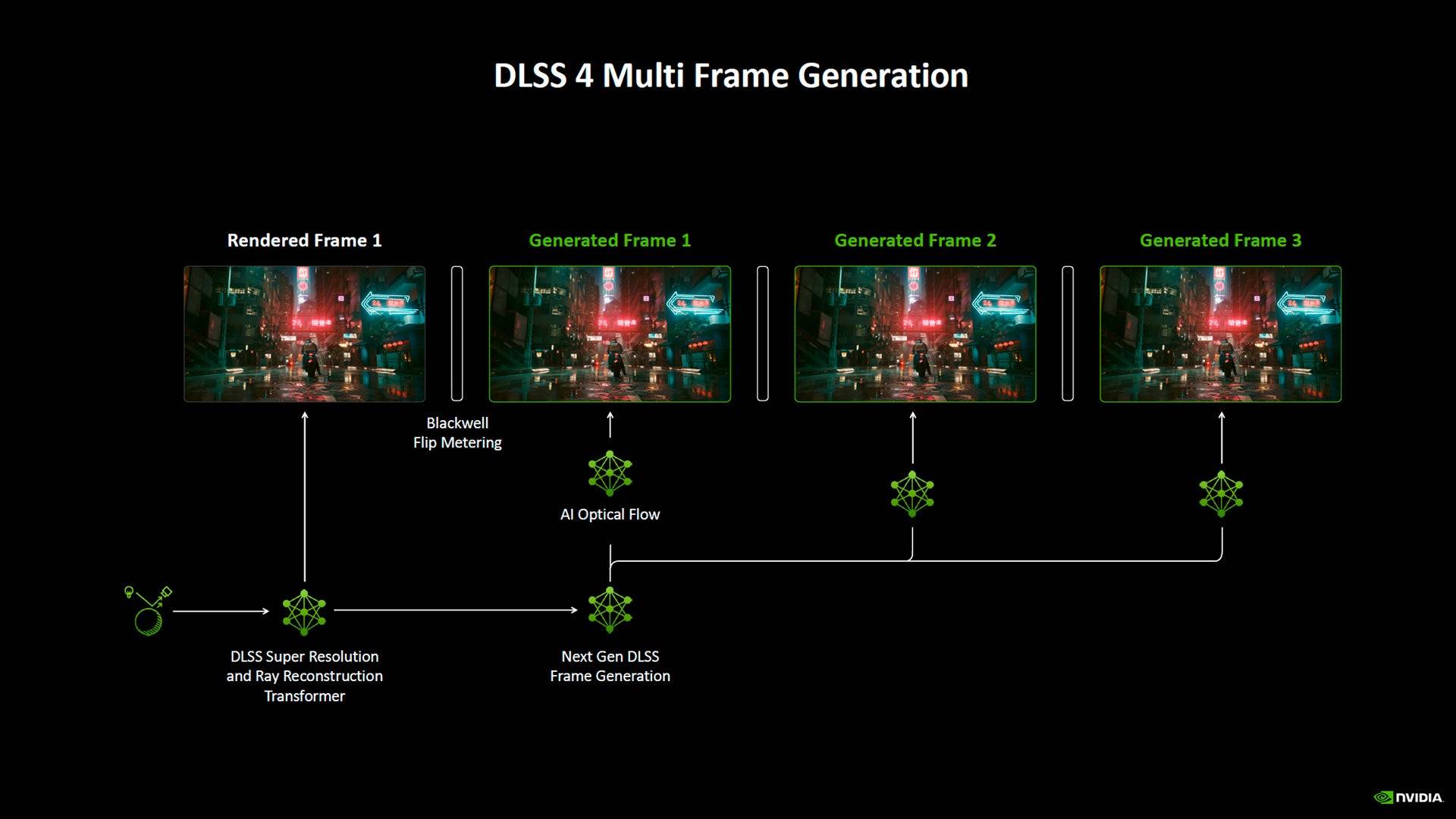
According to Nvidia, the AMP and 5th-generation Tensor Cores enable a 40% faster frame generation model using 30% less memory. This model generates 3 AI frames per rendered frame, and a Flip Metering algorithm minimizes input lag. Nvidia claims this is why multi-frame generation doesn't work on RTX 4000 cards, due to the previous generation's reliance on the CPU for frame pacing, introducing more latency.
This isn't a magic bullet; it's most effective with already decent frame rates. Enabling it with low base frame rates can cause significant latency. Pairing it with DLSS upscaling maximizes performance.
At launch, DLSS 4 supported a wide range of games already supporting DLSS 3 Frame Generation. Testing revealed surprisingly good results in Cyberpunk 2077 and Star Wars Outlaws (beta builds). In Cyberpunk 2077 at 4K with Ray Tracing Overdrive and DLSS Performance mode, the RTX 5090 achieved 94 fps, increasing to 162 fps with DLSS 2x frame generation and 286 fps with 4x frame generation. Similar results were seen in Star Wars Outlaws, reaching around 300 fps with DLSS 4.
Multi-Frame Generation proved effective, with minimal artifacts observed. However, high-end 4K displays are necessary to fully benefit from this technology. Further testing across a wider range of games is needed for a complete assessment.
RTX 5090 – Performance
The Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 is incredibly powerful, but testing presented challenges. 3DMark benchmarks showed a generational improvement over the RTX 4090. However, real-world game testing revealed CPU bottlenecks, even at 4K, with a Ryzen 7 9800X3D CPU. For those with high-end graphics cards, the upgrade might not be transformative; the games aren't fully optimized yet. This is a future-proof investment for upcoming titles.
DLSS 4 was disabled for comparative benchmarks, using public drivers (Nvidia 566.36 and AMD Adrenalin 24.12.1). Games were tested on their latest public builds.
Test System:
- CPU: AMD Ryzen 7 9800X3D
- Motherboard: Asus ROG Crosshair X870E Hero
- RAM: 32GB G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo @ 6,000MHz
- SSD: 4TB Samsung 990 Pro
- CPU Cooler: Asus ROG Ryujin III 360
In 3DMark, the RTX 5090 was up to 42% faster than the RTX 4090 (Speed Way: 14,399 vs 10,130; Port Royal: 36,946 vs 25,997). Compared to the RTX 3090, the performance jump was 2.5x. However, real-world gaming performance tells a different story.
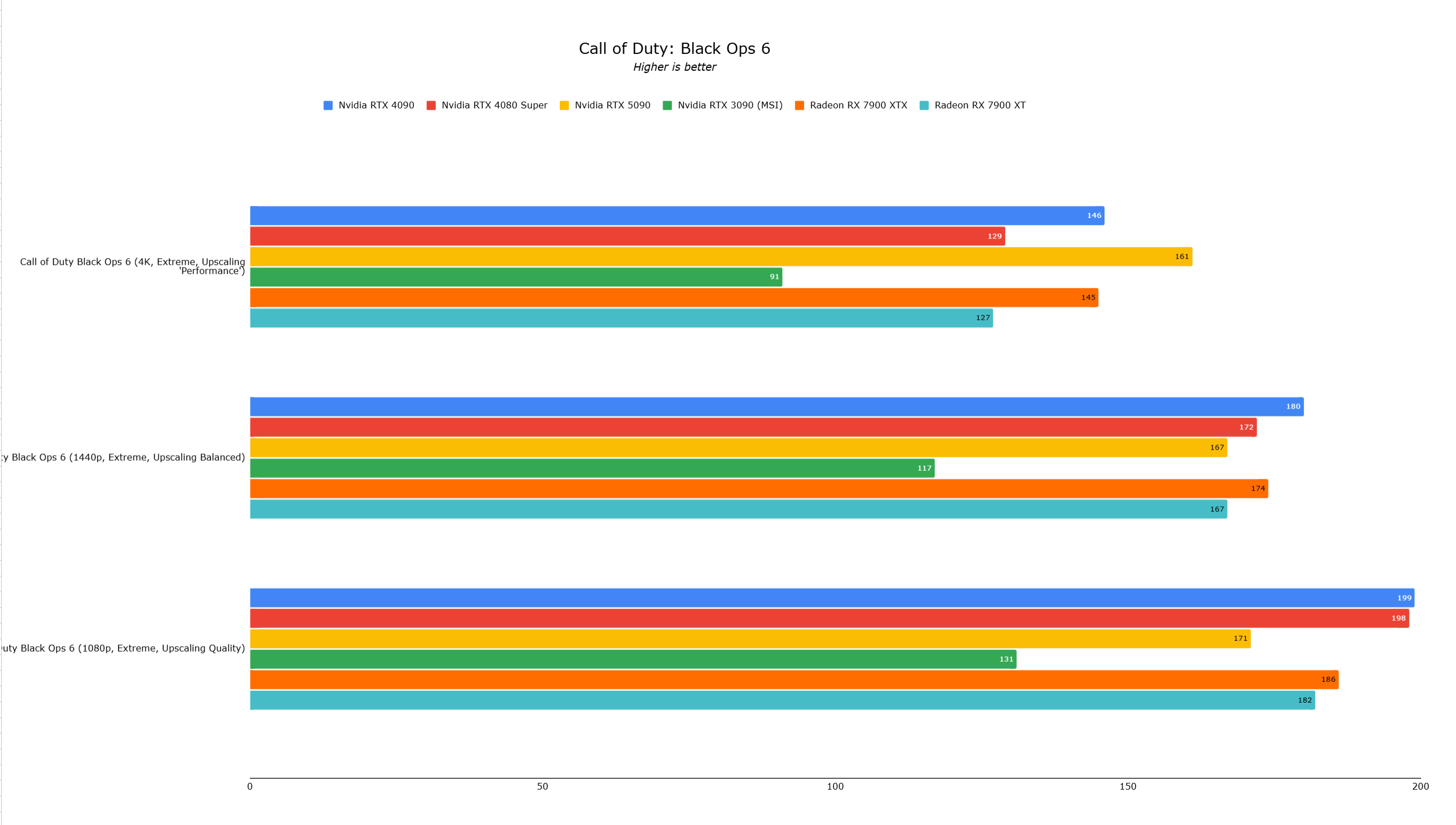
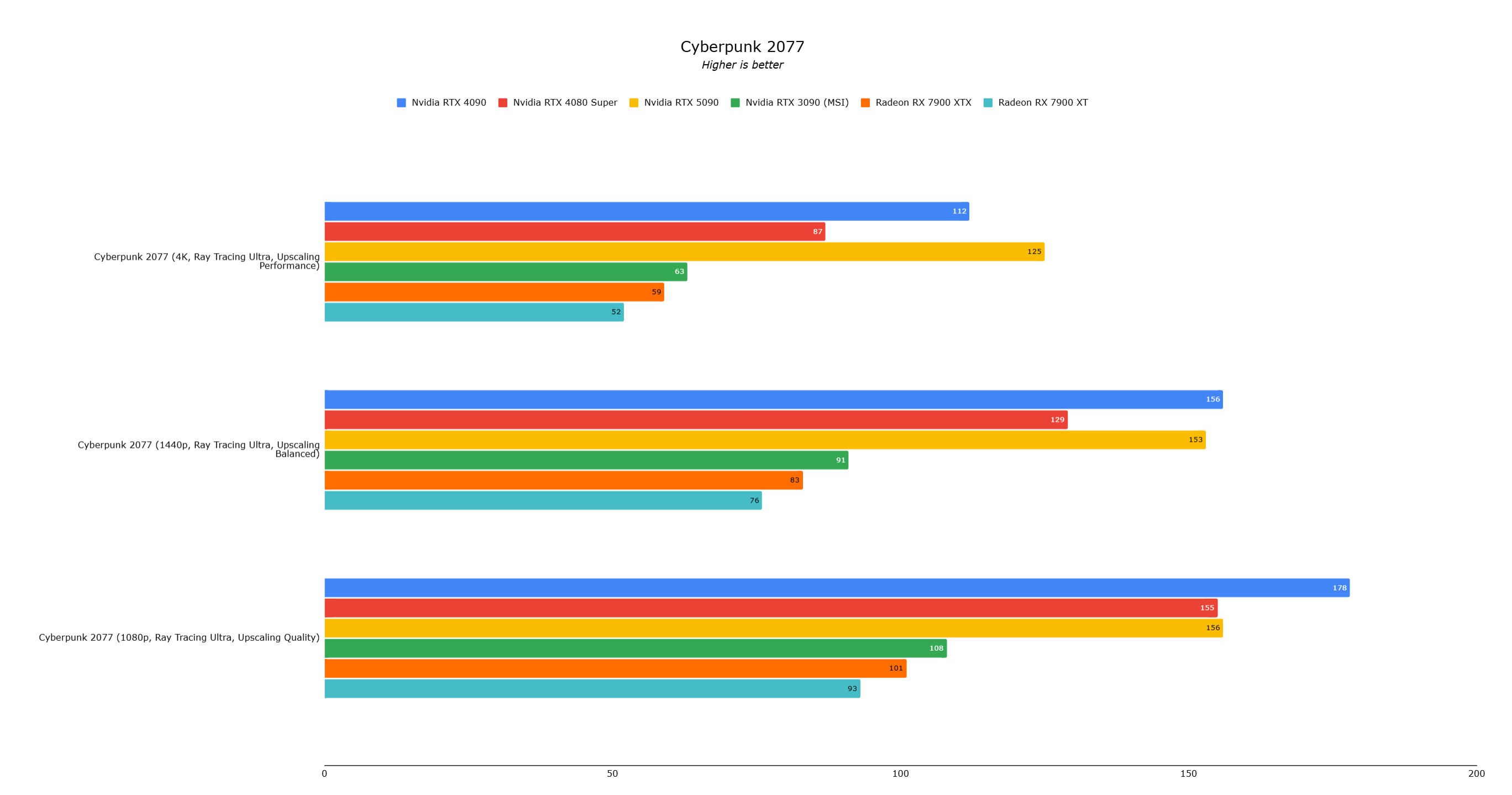
Call of Duty Black Ops 6 showed a severe CPU bottleneck at 4K Extreme settings with DLSS Performance mode (RTX 5090: 161 fps, RTX 4090: 146 fps—a mere 10% difference). Cyberpunk 2077 also showed a similar 10% improvement at 4K with Ray Tracing Ultra and DLSS Performance mode. Lower resolutions showed even less improvement.
Metro Exodus: Enhanced Edition (DLSS disabled) provided a more demanding test, with the RTX 5090 achieving 95 fps at 4K Extreme, compared to 76 fps for the RTX 4090 and 44 fps for the Radeon RX 7900 XTX. This represents a 25% improvement over the RTX 4090.
Red Dead Redemption 2 (4K maxed settings, DLSS Performance) showed a minimal 6% performance uplift (RTX 5090: 167 fps, RTX 4090: 151 fps).
Total War: Warhammer 3 (no ray tracing or upscaling) showed a 35% performance improvement (RTX 5090: 147 fps, RTX 4090: 107 fps).
Assassin's Creed Mirage results were anomalous, likely due to a driver bug, showing lower performance than the RTX 4090.
Black Myth: Wukong showed a 20% improvement (RTX 5090: 104 fps, RTX 4090: 84 fps) at 4K with Cinematic Preset and DLSS 40%.
Forza Horizon 5 showed negligible differences (RTX 5090: 216 fps, RTX 4090: 210 fps).
Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 – Benchmarks
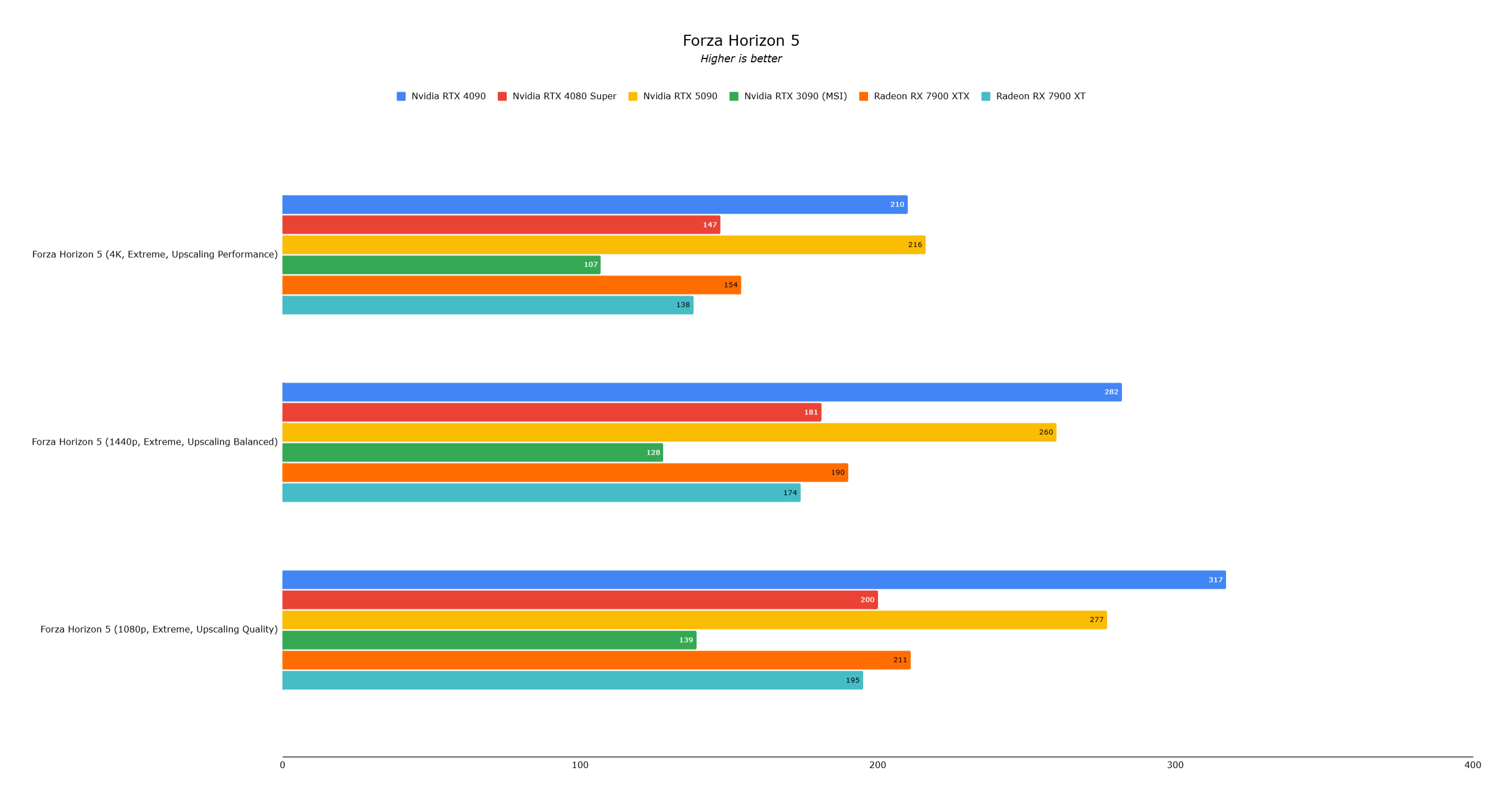
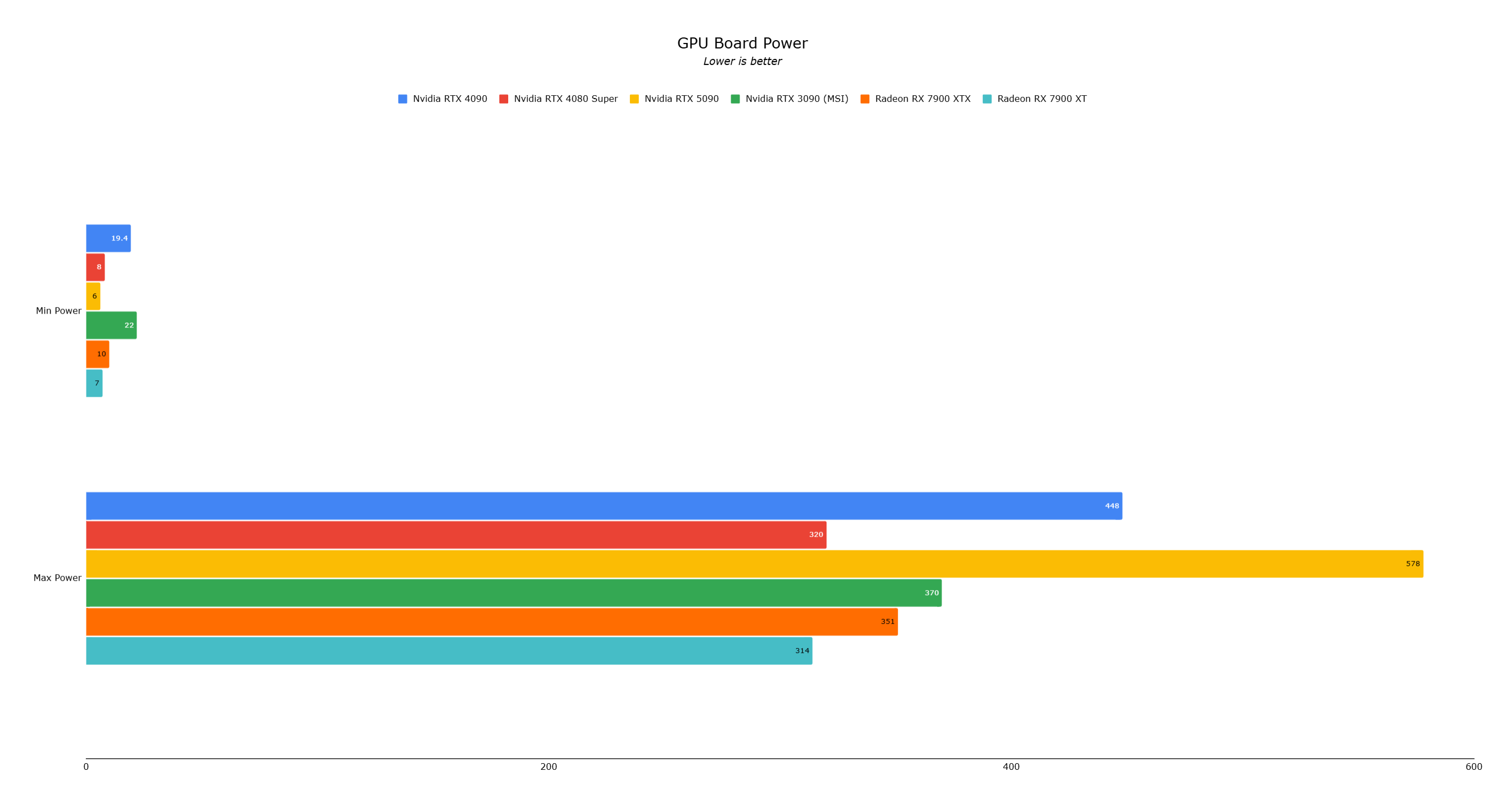
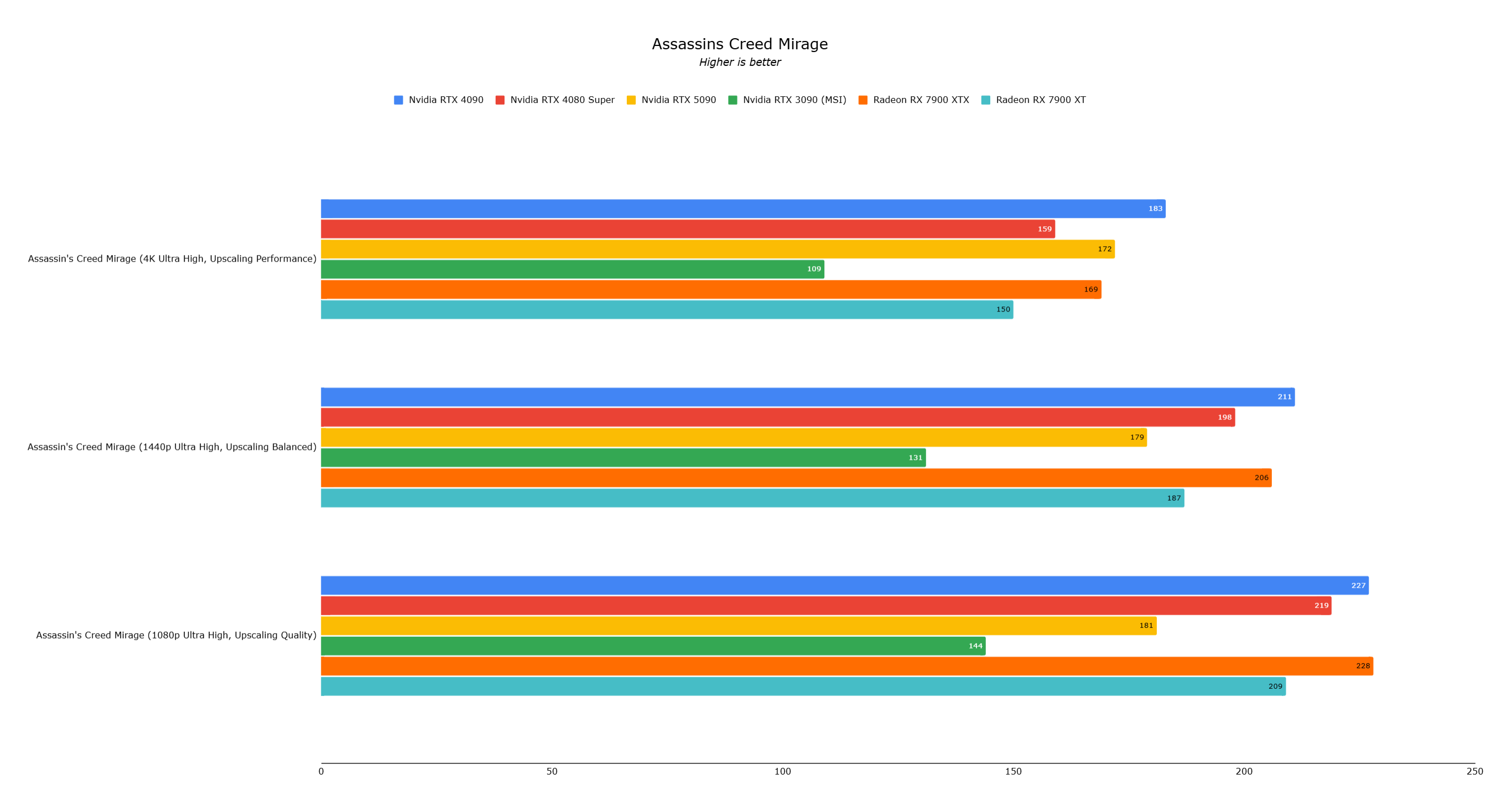








The RTX 5090, while the fastest consumer graphics card, doesn't always deliver a generational leap over the RTX 4090 in current games due to CPU bottlenecks. Its future lies in AI-powered gaming. DLSS 4's frame generation is impressive but requires high-end displays and sufficient base performance. For most, the RTX 4090 remains sufficient for several years. The RTX 5090 is a cutting-edge investment for those embracing the future of AI in gaming.
AnswerSee Results























![FurrHouse [Ch. 3]](https://images.dshu.net/uploads/30/1719555089667e54115d59f.jpg)




